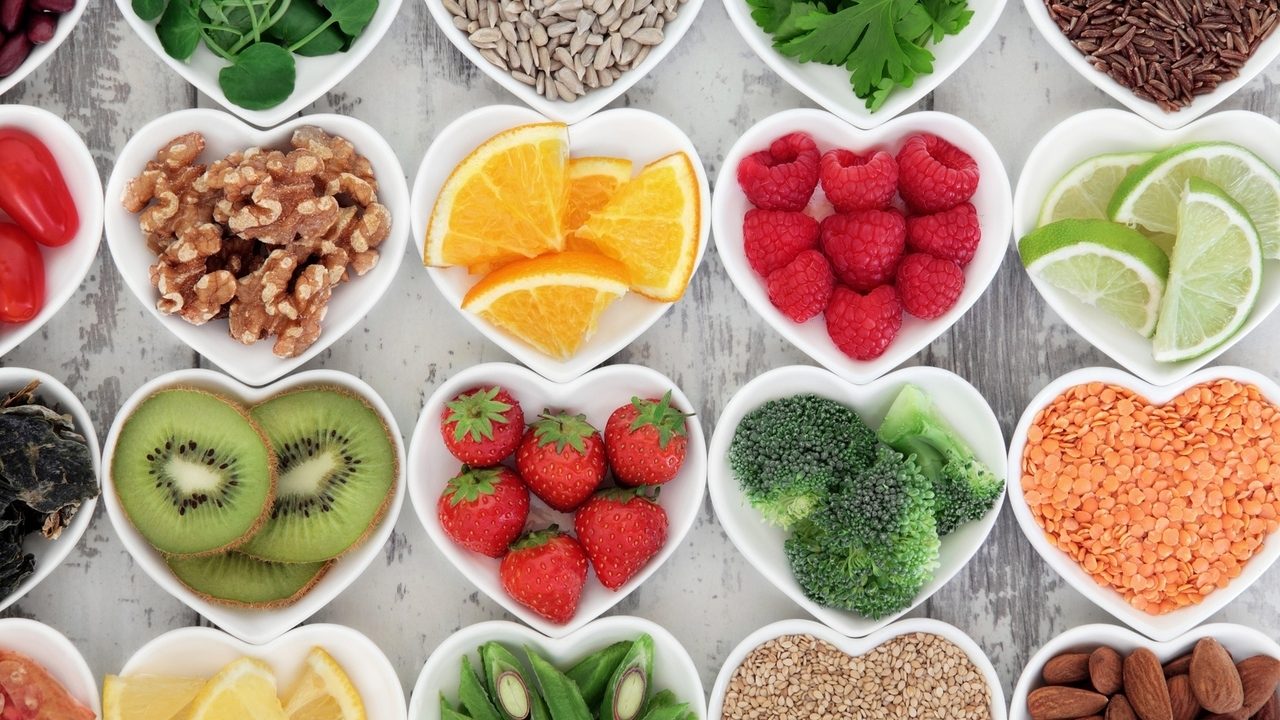
,Proteins are the vital building blocks that our bodies depend on for optimal health. As fundamental components, proteins contribute significantly to the proper functioning and maintenance of muscles, organs, and the immune system.
Understanding the importance of protein in our daily diet is akin to recognizing the key to a healthy and thriving body. In this brief exploration, we'll delve into the significance of daily protein intake, shedding light on how it serves as the ,essential fuel for overall well-being.
Whether you're seeking to fortify your muscles or boost your immune system, the right amount of protein each day is the cornerstone of a robust and resilient body.
Understanding Protein
Definition and Role of Proteins in the Body
Proteins, the dynamic architects of our physiological processes, are essential molecules in the human body.
These intricate structures, comprised of amino acids, serve as the fundamental building blocks crucial for the construction, repair, and regulation of tissues and organs. From immune support to facilitating biochemical reactions, proteins play a multifaceted role in maintaining our health.
Different Types of Proteins (Complete vs.
Incomplete) and Their Sources
- Complete Proteins: Complete proteins, abundant in animal sources like meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy, offer a comprehensive array of essential amino acids. These amino acids, not produced by the body, are crucial for various bodily functions, making complete proteins an integral part of a balanced diet.
- Incomplete Proteins: Contrarily, incomplete proteins, commonly found in plant sources such as legumes, grains, nuts, and seeds, lack certain essential amino acids. However, strategic combinations of these plant-based sources can create a synergistic amino acid profile, ensuring a well-rounded protein intake.
By embracing the complexity of proteins and discerning the nuances between complete and incomplete sources, we empower ourselves to make dietary choices that harmonize with our body's intricate needs.
How Much Protein Do You Need?
Factors Influencing Daily Protein Requirements (Age, Sex, Activity Level, Goals)
Determining your daily protein needs is a personalized journey. Various factors contribute to the optimal amount tailored to your unique circumstances.
- Age:
- Protein requisites shift through life stages.
Children, teenagers, pregnant individuals, and seniors all have distinct protein needs, supporting growth, development, and maintenance.
- Sex:
- Biological distinctions affect protein requirements. Men, typically possessing greater muscle mass, might have different protein needs compared to women.
- Activity Level:
- The more active your lifestyle, the greater the demand for protein. Athletes and those engaged in regular exercise benefit from elevated protein intake to aid muscle repair and recovery.
- Goals:
- Tailoring protein intake to specific goals is pivotal. Whether aiming for muscle gain, weight loss, or overall health, aligning protein consumption with objectives optimizes outcomes.
Understanding and adapting to these influencing factors ensures a protein intake that harmonizes with your body's unique demands.
Recommended Daily Protein Intake Guidelines from Health Organizations
Reliable guidelines from esteemed health organizations act as compass points for daily protein intake, preventing deficiencies and fostering overall well-being.
- World Health Organization (WHO):
- WHO suggests a baseline of 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day for adults, forming a foundation against protein deficiency.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH):
- NIH proposes a protein intake range of 10-35% of daily calories, tailoring recommendations to factors like age, sex, and activity level.
- American Dietetic Association (ADA):
- ADA provides comprehensive guidelines catering to diverse life stages and health objectives, offering personalized insights into optimal protein intake.
These guidelines, though robust, serve as starting points.
Individuals may refine protein intake based on unique circumstances, benefitting from professional advice for personalized recommendations.
Benefits of Meeting Daily Protein Goals
Muscle Growth and Repair
Meeting your daily protein goals is instrumental in promoting muscle growth and facilitating effective repair. Proteins are the building blocks essential for the development and maintenance of muscle tissues. Whether you're an athlete aiming to enhance performance or an individual looking to stay physically active, adequate protein intake supports the body's ability to recover and strengthen muscles.
Weight Management and Satiety
Protein plays a key role in weight management by promoting a feeling of fullness or satiety. Including an adequate amount of protein in your diet can help control appetite and reduce overall calorie intake.
This, in turn, can contribute to weight loss or weight maintenance, making protein an essential component of a balanced and satisfying diet.
Immune System Support
Proteins are integral to the proper functioning of the immune system. They contribute to the production of antibodies, which play a crucial role in defending the body against infections and illnesses. Meeting your daily protein goals helps fortify your immune system, providing a robust defense mechanism to combat pathogens and maintain overall health.
Hormone Regulation and Enzyme Production
Proteins are involved in the synthesis of hormones and the production of enzymes, both of which are essential for various physiological processes.
Hormones regulate key functions in the body, including metabolism and growth, while enzymes facilitate biochemical reactions. By meeting your daily protein goals, you support the intricate balance of hormones and ensure the availability of enzymes necessary for maintaining optimal health.
Incorporating sufficient protein into your daily diet not only aids in achieving specific health and fitness goals but also contributes to overall well-being by supporting vital bodily functions.
Sources of High-Quality Proteins
Animal-Based Protein Sources
- Meat, Poultry, and Fish:
- Meat, poultry, and fish are rich sources of complete proteins, providing all essential amino acids necessary for the body.
Options such as lean cuts of beef, chicken, turkey, and various types of fish offer not only protein but also essential nutrients like iron and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Dairy Products:
- Dairy products, including milk, yogurt, and cheese, are excellent sources of high-quality protein. They also provide essential calcium for bone health. Opt for low-fat or Greek yogurt for an additional protein boost with reduced fat content.
- Eggs:
- Eggs are a versatile and nutrient-dense protein source, offering all essential amino acids. They are also rich in vitamins and minerals, making them a wholesome addition to a balanced diet.
Plant-Based Protein Sources
- Legumes and Beans:
- Legumes and beans, such as lentils, chickpeas, black beans, and kidney beans, are excellent plant-based protein sources.
They are not only high in protein but also fiber, promoting digestive health. Incorporating a variety of legumes into your diet ensures a diverse amino acid profile.
- Nuts and Seeds:
- Nuts and seeds, including almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds, are nutrient-dense sources of plant-based proteins. Additionally, they provide healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals, offering a well-rounded nutritional profile.
- Grains and Vegetables:
- Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats, as well as certain vegetables like spinach, broccoli, and peas, contribute to your daily protein intake. While individual plant-based sources may lack some essential amino acids, combining different foods throughout the day ensures a complete and balanced protein intake.
Incorporating a variety of both animal-based and plant-based protein sources into your diet allows you to enjoy the benefits of diverse nutrients while meeting your daily protein requirements.
Whether you follow a carnivorous or plant-focused diet, choosing high-quality protein sources is key to supporting overall health and well-being.
Balancing Macronutrients
The Role of Protein in a Well-Rounded Diet
Protein plays a pivotal role in creating a well-rounded and nutritious diet that supports overall health and vitality. Acting as the building blocks for tissues, enzymes, and hormones, protein is indispensable for the body's structure and function. Including an adequate amount of protein in your diet contributes to muscle development, tissue repair, and the maintenance of essential bodily functions.
Proteins provide a sustained source of energy, making them a crucial component for individuals engaging in physical activities or those aiming for weight management.
Additionally, the satiety effect of protein can help regulate appetite, reducing the likelihood of overeating and contributing to a balanced caloric intake.
In a well-rounded diet, protein complements other macronutrients, such as carbohydrates and fats, to create a synergistic balance that optimizes energy levels, supports metabolic functions, and fosters overall well-being.
Finding the Right Balance Between Proteins, Carbohydrates, and Fats
Achieving an optimal balance among macronutrients—proteins, carbohydrates, and fats—is essential for maintaining a healthy and sustainable diet. Each macronutrient serves a distinct purpose in the body, and finding the right proportions ensures a harmonious relationship that meets your nutritional needs.
- Proteins:
- Aim for a diverse range of protein sources, including lean meats, dairy products, legumes, and plant-based alternatives.
Incorporating proteins in each meal supports muscle development, enhances metabolism, and promotes a feeling of fullness.
- Carbohydrates:
- Include complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to provide a steady source of energy. These carbohydrates are rich in fiber, aiding digestion and promoting a feeling of satiety.
- Fats:
- Choose healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats contribute to brain health, help absorb fat-soluble vitamins, and play a role in hormone production.
Finding the right balance involves considering individual factors such as age, activity level, and health goals. A balanced macronutrient intake supports metabolic efficiency, regulates blood sugar levels, and fosters long-term health.
Remember, achieving nutritional balance is not about strict ratios but about understanding and fulfilling your body's unique requirements.
Consultation with a registered dietitian or nutritionist can provide personalized guidance to help you strike the optimal balance for your specific needs and goals.
Potential Risks of Inadequate Protein Intake
Impact on Muscle Mass and Strength
Insufficient protein intake poses a significant risk to muscle mass and strength.
Proteins serve as the fundamental building blocks essential for muscle repair and maintenance.
Without an ample supply, the body may struggle to regenerate lean muscle tissue, leading to muscle atrophy, weakness, and a decline in overall physical performance.
Compromised Immune Function
A deficiency in protein intake jeopardizes the proper functioning of the immune system. Proteins, crucial for the production of antibodies, are integral to the body's defense against infections and diseases.
Inadequate protein can impede antibody production, heightening susceptibility to illnesses and weakening the body's ability to mount an effective immune response.
Effects on Overall Health and Well-being
Inadequate protein intake has far-reaching consequences for overall health and well-being. Proteins are involved in diverse physiological processes, including the synthesis of enzymes, hormones, and neurotransmitters.
A deficiency can disrupt these processes, affecting metabolic function, mood regulation, and cognitive performance.
To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to ensure a sufficient and well-balanced protein intake tailored to individual needs, considering factors such as age, activity level, and health goals. This approach contributes to maintaining optimal muscle function, immune resilience, and overall well-being.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Protein Intake
Tracking Protein Intake Through Food Journals or Apps
- Food Journal:
- Consider using a traditional food journal like the "Moleskine Passion Journal - Wellness." This stylish and portable journal allows you to log your daily protein intake along with other nutritional details.
It's a tactile and convenient way to keep track of your dietary habits.
- Nutrition Tracking App:
- For a tech-savvy approach, try the "MyFitnessPal" app. This widely-used app allows you to log your daily food intake, including proteins, and provides nutritional insights. It also offers a barcode scanner for easy input, making it a convenient tool for those who prefer digital tracking.
Both of these tools provide efficient ways to monitor your protein intake, helping you stay accountable to your dietary goals.
Making Adjustments Based on Fitness Goals and Health Status
Adjusting your protein intake requires a thoughtful approach aligned with your fitness goals and health status.
- Fitness Goals:
- For those aiming to increase muscle mass or enhance athletic performance, consider incorporating a high-quality protein supplement like "Orgain Organic Protein Powder." It's a plant-based protein option with a blend of pea protein, brown rice protein, and chia seeds, catering to various fitness goals.
- Health Status:
- If you have specific health considerations, a specialized protein source like "Isopure Zero Carb Protein Powder" may be suitable. It's a low-carb, lactose-free option that can be beneficial for individuals with dietary restrictions or sensitivities.
Always consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant adjustments to your protein intake, especially if you have underlying health conditions or dietary restrictions.
These products can complement a balanced diet, supporting your fitness goals and overall well-being.
Special Considerations
Protein Needs for Athletes and Active Individuals
Athletes and individuals engaged in regular physical activity have unique nutritional requirements, and ensuring adequate protein intake is vital for optimizing performance, recovery, and overall well-being.
Increased Protein Demands:
- Athletes and active individuals often have higher protein requirements due to the constant wear and tear on muscles during physical exertion. Protein serves as the primary building block for muscle repair and growth, making it essential to support the demands of regular exercise.
Protein Timing:
- Timing protein intake strategically around workouts can enhance its effectiveness. Consuming protein both before and after exercise helps maximize muscle protein synthesis, facilitating better recovery and adaptation to training stress.
Protein Sources:
- Including a variety of protein sources in the diet is key for meeting the increased demands. Animal-based sources like lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products provide complete proteins with all essential amino acids.
Plant-based sources such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains contribute to a diverse amino acid profile.
Protein Supplements:
- While whole foods should be the primary source of protein, some athletes may incorporate protein supplements for convenience or to meet specific dietary needs.
- Protein powders, shakes, and bars can be convenient options, but they should complement a well-rounded diet rather than replace whole food sources. Here are some recommended supplements that will complement your diet:
- Whey Protein Isolate:
- For athletes looking for a quick and easily digestible protein source, "Optimum Nutrition Gold Standard 100% Whey Protein Isolate" is a popular choice. It provides a high-quality protein boost to aid muscle recovery after intense workouts.
- Plant-Based Protein Blend:
- Plant-based athletes may prefer "Vital Proteins Performance Protein." This blend combines pea protein, collagen, and BCAAs, offering a comprehensive amino acid profile crucial for muscle repair and growth.
These supplements can be valuable additions to the diets of athletes and active individuals, ensuring they meet their increased protein needs for optimal performance and recovery.
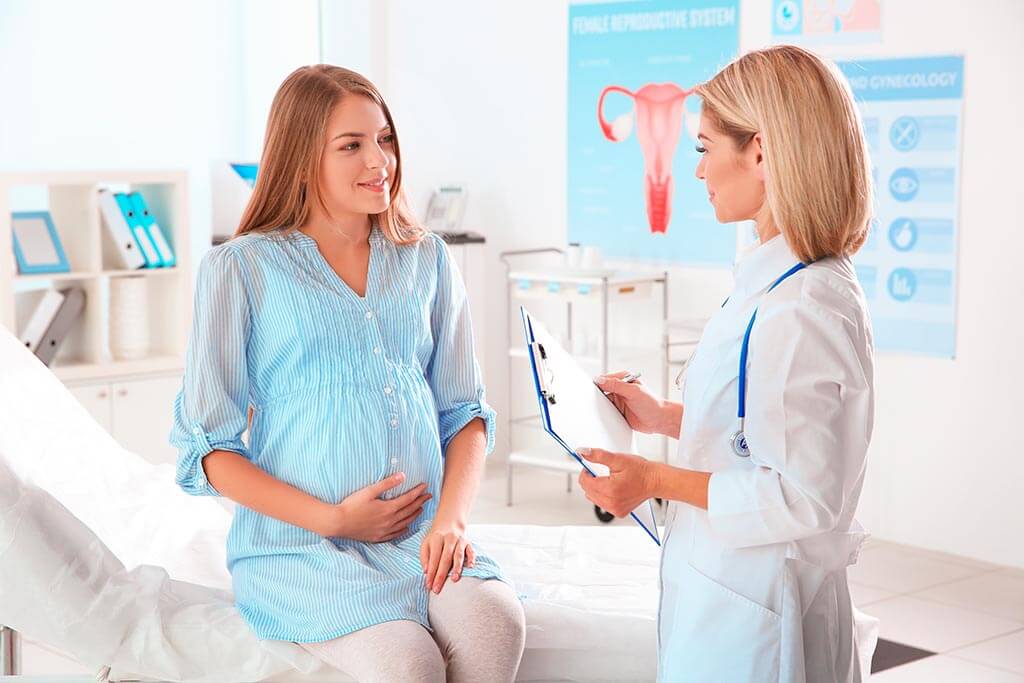
Protein Requirements During Specific Life Stages (Pregnancy, Elderly)
Protein Requirements During Specific Life Stages
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a transformative period when the body undergoes substantial changes to support the growth and development of the baby. Adequate protein intake is crucial during this stage to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus.
- Increased Protein Intake:
- Pregnant women often need additional protein to support the growth of the placenta, amniotic fluid, and the developing fetal tissues.
The recommended protein intake during pregnancy typically increases, emphasizing the importance of incorporating protein-rich foods into the diet.
- Complete Proteins:
- Including complete proteins in the form of lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products is essential. These sources provide all the essential amino acids necessary for the development of the baby's organs, muscles, and other vital tissues.
- Plant-Based Proteins:
- Plant-based protein sources such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains can also contribute to meeting increased protein needs. Combining a variety of plant-based proteins helps ensure a diverse amino acid profile.
Elderly
As individuals age, maintaining muscle mass and overall health becomes paramount. Protein requirements for the elderly are influenced by factors such as muscle loss, reduced absorption efficiency, and changes in metabolism.
- Protein for Muscle Health:
- Older adults often experience a gradual decline in muscle mass and strength, known as sarcopenia.
Adequate protein intake, combined with resistance exercise, can help mitigate muscle loss and support overall mobility and functionality.
- Diverse Protein Sources:
- Including a variety of protein sources in the diet is crucial for the elderly. This includes lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy products, legumes, and plant-based options. Diversifying protein sources ensures a well-rounded intake of essential amino acids and other nutrients.
- Protein Timing:
- Distributing protein intake evenly throughout the day, rather than consuming large amounts in one meal, may be beneficial for the elderly. This approach supports optimal muscle protein synthesis and overall protein utilization.
In both pregnancy and older age, personalized nutritional advice from healthcare
professionals, including registered dietitians, can provide guidance tailored to individual needs and health conditions.
Prioritizing a balanced and protein-rich diet during these life stages contributes significantly to overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
Recap of the Importance of Daily Protein Intake
In summary, daily protein intake is vital for numerous physiological functions, from muscle growth to immune system support.
Understanding these roles underscores the importance of incorporating proteins into our daily diets.
As you strive for optimal health, make informed choices tailored to your needs. Whether you're an athlete, expectant mother, or navigating aging, conscious protein intake plays a crucial role. Choose diverse protein sources, track your intake, and consult experts for personalized guidance.
Embrace the power of informed choices for a healthier and vibrant life.
Original Article